Lorig Taxonomy
Based on their clinical experiences and review of the literature, Lorig and colleagues identified six core components of SM: problem-solving, decision-making, resource utilization, taking action, and self-tailoring. Each component is described in detail in Table 6.
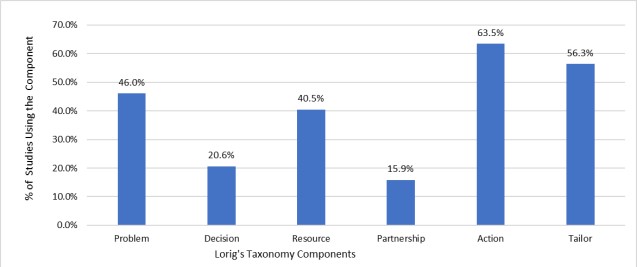
Figure 3 shows the percentage of studies included in this review using each of the components from Lorig’s taxonomy. Under Lorig’s Taxonomy of SM program components, taking action is the most prevalent component in the SM programs for SCI reviewed in this chapter, utilized in 63.5 % of the program. In addition, more than half (53.6%) of the programs involved the self-tailoring component. While the management of secondary health conditions post SCI often requires the collaboration between patients and healthcare providers, forming patient-healthcare provider partnership was the least frequently used component, only present in 15.9% of the SM programs.